In online business, dropshipping and private label catch the eye of budding entrepreneurs. That is the reason we have prepared a blog on dropshipping vs private label.
For instance, dropshipping and private label offer many perks. Like low initial costs and the freedom to work from anywhere with internet access.
Table of Contents
However, they differ in many things. Such as profit margins, branding control, shipping logistics, and overall business control. Let’s explore these distinctions to find the right eCommerce model for your journey.
Before we start here is a market insight for Dropshipping vs Private Label:
| Feature | Dropshipping | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size | Large and growing | Significant segment within e-commerce |
| Growth Rate | High | Steady |
| Profit Margins | Lower (10-25%) | Higher (20-40%) |
| Ease of Entry | Easier (low initial investment) | More complex (higher upfront costs) |
What Is Dropshipping?
One approach to retail order fulfillment is dropshipping. Where a retailer doesn’t keep track of his product inventory.
Rather, goods are obtained from outside vendors who take care of both the final customer’s shipping and storage.
This removes the requirement for business owners to make significant investments in inventory control and warehousing. making dropshipping a desirable choice for people looking to enter the e-commerce market with little risk.
Know more: What is Dropshipping? How does it work? Pros and Cons
How Dropshipping Works?
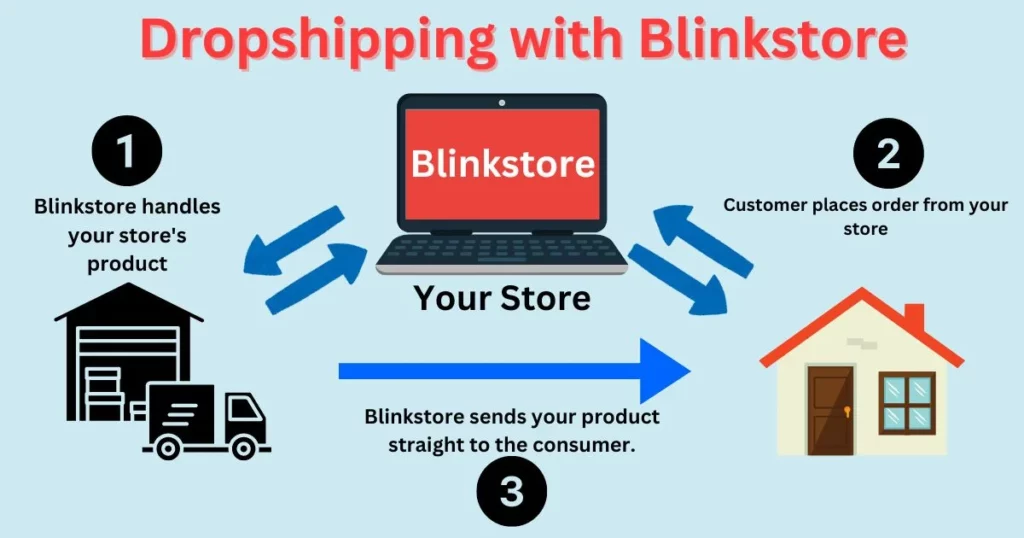
Dropshipping works by following a straightforward process:
Customer Places Order: A customer buys from your online store.
Order Sent to Supplier: You send order details to your supplier, including the customer’s address.
Supplier Ships Product: The supplier packs and sends the product to the customer.
You Make Money: The difference between what you paid the supplier and what the customer paid is what you keep.
In short, you’re the link between the customer and supplier, managing sales and service while the supplier deals with inventory and shipping.
Learn more: How to Start Dropshipping for Free in 2024 – Complete Guide
Pros of Dropshipping
Very low startup costs
- Try your hand at eCommerce without going over budget.
Easy to get started and test products
- Experiment with different products and niches without committing to large inventories.
No inventory or shipping to manage
- Focus on sales and marketing without the hassle of inventory management or fulfillment.
Cons of Dropshipping
Low profit margins
- Despite low overhead, profit margins can be tight.
No control over shipping times/costs
- Shipping delays or cost fluctuations are out of your hands.
No branding control or ownership
- Your brand identity is at the mercy of your suppliers.
What is Private Labeling?

Private labeling is when a maker produces goods and sells them under a store’s brand. The maker creates the product, but it’s sold under the store’s name. This lets stores sell products without making them.
Many industries, like food and clothes, use private labeling. It helps with being unique, controlling prices, and branding.
How Private Label Works?
Private labeling happens when a manufacturer partners with a retailer or another company. Here’s how it usually goes:
Manufacturing: The maker creates goods based on the retailer’s or company’s instructions.
Branding: The products get labeled and packaged with the retailer’s or company’s name, not the maker’s.
Distribution: The retailer or company sends the products to customers through their own stores, websites, or networks.
Sales and Marketing: The retailer or company sells and advertises the products with their brand, often with other items they sell.
Customer Interaction: Shoppers buy the products, usually without knowing they’re made by someone else since they’re labeled with the retailer’s name.
Feedback and Improvement: The retailer might ask customers for feedback and collaborate with the maker to enhance or create new products.
In summary, private labeling lets retailers or companies offer various products without making them, and it also allows for custom branding to suit their market needs.
Pros of Private Label
Higher profit margins
- Gain more authority over profit margins and pricing.
Ownership and control over the brand
- Craft your brand’s identity and narrative to resonate with your target audience.
Control over shipping and packaging
- Delight customers with personalized packaging and fast shipping.
Cons of Private Label
Higher startup costs
- Investing in inventory and branding requires more significant upfront capital.
Need to handle shipping/inventory
- It can take a lot of time and effort to manage fulfillment and inventory.
Sourcing quality suppliers can be challenging
- Finding reliable suppliers who meet your quality standards may require thorough research and vetting.
Dropshipping vs Private Label: Key Differences Between Them
Dropshipping and private label are two distinct eCommerce models with key differences:
1. Ownership
Dropshipping: You act as a middleman, connecting customers with suppliers, but you don’t own the products.
Private Label: You own the products, as they are manufactured specifically for your brand.
2. Branding Control
Dropshipping: Limited control over branding since products are supplied by others.
Private Label: Complete control over branding, allowing you to establish a unique brand identity.
3. Profit Margins
Dropshipping: Typically lower profit margins due to intense competition and reliance on supplier pricing.
Private Label: Generally higher profit margins as you set the prices and control the product quality.
4. Shipping Logistics
Dropshipping: Suppliers handle shipping logistics, including packaging and delivery.
Private Label: You manage shipping logistics, allowing for more control over delivery times and customer experience.
5. Startup Costs
Dropshipping: Minimal upfront investment is required since you don’t need to purchase inventory.
Private Label: Higher initial investment is needed for product development, inventory, and branding efforts.
You can use these distinctions to determine which eCommerce model best suits your needs in terms of control level, budget, and business objectives.
Dropshipping vs Private Label: Similarities Between Them

While dropshipping and private label are distinct eCommerce models, they do share some similarities:
1. No Inventory Management
Both models allow businesses to operate without the need to hold inventory. In dropshipping, you don’t need to invest in or manage inventory upfront, while in private label, the manufacturer handles inventory management.
2. Low Startup Costs
Both dropshipping and private label offer relatively low startup costs compared to traditional retail models. Dropshipping requires minimal investment since you don’t need to purchase inventory upfront.
While private label may require some initial investment for product development and branding but are still generally lower than setting up manufacturing facilities.
3. Flexibility
Both models offer flexibility in terms of product selection and scalability. Dropshipping allows you to easily test different products and niches without committing to large inventories, while private label enables you to customize products to suit your brand and target market.
4. Outsourcing Manufacturing
In both models, the actual manufacturing of the products is outsourced to third-party suppliers. In dropshipping, suppliers fulfill orders directly to customers, while in private label, manufacturers produce products according to your specifications.
What is Private Label Dropshipping?

Private Label Dropshipping is a business setup where you design your own brand for the products you market. This grants you enhanced control over your offerings, fostering a more robust brand identity.
Why not bring best of the both?
Private Label Dropshipping: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Brand Ownership: With private label dropshipping, you’re in charge of your brand. You can create a unique brand identity, get known, and keep customers coming back under your brand name.
- Customization: Private label dropshipping lets you customize a lot. You can tweak products, packaging, and branding to match your style and what customers want.
- Higher Profit Margins: Compared to regular dropshipping, private label dropshipping can make you more money. Selling stuff under your own brand lets you charge higher prices and boost profits.
- Brand Recognition: Over time, private label dropshipping can get your brand noticed. As more people know and trust your brand, you’ll see more repeat buyers and referrals.
Cons:
- Initial Investment: Getting into private label dropshipping costs a lot upfront. You’ll need to spend on branding, marketing, and product development, even hitting minimum order quantities for custom stuff.
- Inventory Management: Keeping track of what you have in stock can be hard. Dealing with storage, tracking, and running out of stuff can bump up costs and make things complicated.
- Quality Control: Making sure every product is top-notch can be tough. Problems with quality or getting orders filled might pop up, hurting your brand and how much people trust it.
- Market Competition: Private label dropshipping is competitive. Going up against big brands and catching customers’ eyes in a crowded market is a challenge. You’ll need smart marketing and ways to stand out.
How Does Private Label Dropship Work?
Private label dropshipping seamlessly combines the strengths of private labeling with the convenience of dropshipping, offering an efficient way to establish your brand presence in the market.
Here’s a simplified guide to help you navigate this process and build a successful business:
1. Research and Planning
Identify a Profitable Niche
Explore market trends to find a niche with high demand and manageable competition. For example, if you’re into fitness, consider athleisure wear or eco-friendly workout gear.
Choose Products
Select products that align with your niche and target audience’s preferences. Conduct keyword research and analyze trends to spot winning products.
Find Reliable Suppliers
Vet dropshipping suppliers carefully. Look for reliability, quality, and competitive pricing. Platforms like Alibaba or SaleHoo can help you discover trusted suppliers.
2. Create Your Brand
Craft a Compelling Brand Identity
Develop a brand that reflects your values and connects with your audience emotionally. Design a memorable logo and choose brand colors and fonts wisely.
Personalize Your Products
Work closely with suppliers to add branded elements to your products. This enhances brand recognition and adds value to your offerings.
Set Up Your Online Store

Choose the Right Platform
Select an e-commerce platform that suits your needs. Blinkstore, WooCommerce, and Shopify are popular choices.
Optimize Your Product Listings
Create captivating product listings with relevant keywords.
Streamline Payment and Shipping
Integrate secure payment gateways and efficient shipping methods for a seamless shopping experience.
4. Marketing and Promotion
Harness Content Marketing
Provide insightful and entertaining content for your audience. Blogs, guides, and videos can help promote your products subtly.
Build a Social Media Presence
Use social media to showcase your products and engage with your audience. Run targeted ad campaigns for better reach.
Forge Influencer Partnerships
Collaborate with influencers in your niche to boost your brand’s credibility and visibility.
5. Customer Service and Support
Customer Service
Provide prompt assistance and multiple support channels to ensure a positive shopping experience.
Establish Clear Return Policies
Define transparent return policies to build trust with your customers.
Seek Customer Feedback
Gather feedback regularly to improve your products and services.
6. Monitor Performance and Iterate
Track Key Metrics
Monitor sales, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction to evaluate your strategies.
Experiment and Optimize
Test different marketing tactics and product offerings to find what works best.
Stay Agile
To keep ahead of the competition, adjust to consumer preferences and market trends.
What is White Label?
White labeling is when a product or service created by one company is sold by another under their own brand. Essentially, the original company makes the product, but it’s marketed and sold under the branding of another company.
This lets companies offer more products without making them themselves. It’s common in industries like software and cosmetics.
How Does White Label Dropshipping Work?
White label dropshipping works much like regular dropshipping but with an emphasis on branding. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Supplier Relationship: As the retailer, you partner with a supplier offering white label products. They manufacture the goods but let you sell them under your brand.
- Product Customization: Collaborate with the supplier to add your branding elements like labels or packaging, making the products seem like your own creation.
- Online Store Setup: You create an online store to display and sell these products, using platforms like Shopify or your website.
- Order Fulfillment: When customers buy from your store, their order details go to the supplier. The supplier ships the product directly to the customer, without any mention of their branding.
- Customer Interaction: Customers purchase from your store and receive the product with your branding, often unaware of the supplier’s involvement.
- Marketing and Customer Service: You handle marketing, customer inquiries, and support, ensuring a positive shopping experience and promoting your white label products effectively.
White Label Dropshipping: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Brand Control: With white label dropshipping, you sell products under your own brand name, establishing a unique identity and gaining recognition among customers.
- Flexibility: White label dropshipping allows customization of packaging, labels, and product design to match your brand’s style and meet customer preferences.
- Scalability: Grow your business quickly with white label dropshipping without investing in inventory or production facilities. Expand your product range and reach new markets easily.
- Reduced Time and Costs: White label dropshipping cuts down on time and costs associated with product development and inventory management, letting you focus on business growth.
Cons:
- Quality Control: Lack of control over product quality is a downside of white label dropshipping. Variation in quality across suppliers may affect customer satisfaction.
- Brand Reputation: Subpar product quality can damage your brand reputation and trust among customers, making it challenging to recover.
- Dependency on Suppliers: Relying on suppliers for sourcing, manufacturing, and fulfillment can lead to issues such as stock shortages or delays, impacting business operations.
- Competition: Intense competition in the market for white label products makes it challenging to differentiate your offerings and stand out, especially if competitors offer similar products at lower prices.
Private Label vs White Label Dropshipping: Which is Best?
Deciding between private label and white label dropshipping depends on your specific business goals, resources, and preferences. Here’s a simple guide to help you:
Private Label Dropshipping
Best For: Entrepreneurs looking to establish a unique brand identity, differentiate themselves in the market, and build long-term customer loyalty.
Advantages: Greater control over branding, customization, and product quality. Higher profit margins due to premium pricing.
Considerations: Requires higher initial investment in branding, marketing, and product development. Involves more complex inventory management and quality control processes.
White Label Dropshipping
Best For: Entrepreneurs seeking a low-risk, low-cost entry into ecommerce with minimal upfront investment and quick setup.
Advantages: Minimal upfront investment required. Quick and easy setup process. Scalable business model with low overhead costs. Reduced risks compared to private label dropshipping.
Considerations: Limited control over branding and customization. Potential for lower profit margins due to higher competition. Reliance on suppliers for product quality and consistency.
Conclusion: Pick the right eCommerce model for you
When deciding between dropshipping and private labeling, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Your choice should align with your goals, skills, and budget.
For low-risk entry into eCommerce, consider dropshipping. But if you crave brand control and the potential for higher profits, private labeling could be the way to go.
Alternatively, explore private label dropshipping for a blend of both. Assess your strengths and preferences to determine the eCommerce approach that fits you best.
FAQs on Dropshipping vs Private Label
Some frequently asked questions about Dropshipping vs Private Label.
Is dropshipping the same as private label?
No, dropshipping and private label are different eCommerce models. Dropshipping involves selling products without holding inventory. While private label involves branding and selling products manufactured by another company under your own brand name.
What is more profitable than dropshipping?
Private labeling is often considered more profitable than dropshipping. With private label, you have greater control over branding, pricing, and profit margins compared to dropshipping.
Is private labeling profitable?
Private labeling can be profitable, especially if you are able to establish a strong brand identity. Offer high-quality products, and effectively market your products to your target audience.
What is the difference between a private label and a reseller?
A private label sells products under its own brand name but manufactured by another company. A reseller, on the other hand, buys goods from a producer or distributor and resells them under the original brand name.
Is private label risky?
Private labeling comes with risks, such as product quality issues, competition, and market fluctuations. However, with proper research, planning, and execution, private labeling can be a successful and profitable business model.
What are the 4 types of private labels?
The four types of private labels are:
– Economy/Private Select: Basic, low-cost products targeting budget-conscious consumers.
– National Brand Equivalent (NBE): Products designed to mimic popular national brands at a lower price point.
– Premium/Private Select: Higher-quality products positioned as premium alternatives to national brands.
– Copycat/Private Copy: Products imitating specific national brand products, often with similar packaging and features.
